Best Practices for CRM and EHR Integration
Integrating CRM and EHR systems can transform how recovery centers manage patient care and operations. By combining clinical data (like diagnoses and treatment plans) with engagement data (such as follow-ups and patient inquiries), these systems eliminate inefficiencies like manual data entry and disconnected workflows. The result? Faster response times, fewer errors, and better patient retention.
Key Takeaways:
- Unified Dashboards: Combine medical history, lab results, and communication logs in one place.
- Compliance: Ensure HIPAA and 42 CFR Part 2 standards with tools like Recovery Center CRM.
- Technical Standards: Use HL7 FHIR and SMART on FHIR for seamless data exchange.
- Data Mapping: Align fields like demographics, diagnoses, and referrals to avoid duplication.
- Stakeholder Involvement: Engage clinical, administrative, and IT teams early to document pain points and set goals.
- Testing & Training: Use sandbox environments for error testing and train staff with role-specific programs.
- Performance Monitoring: Track metrics like no-show rates, system uptime, and data accuracy post-launch.
Denver Health and Pacific Clinics have shown how integration can boost patient retention and save hours of manual work. With clear planning, secure systems, and ongoing improvements, recovery centers can streamline operations while focusing on patient care.
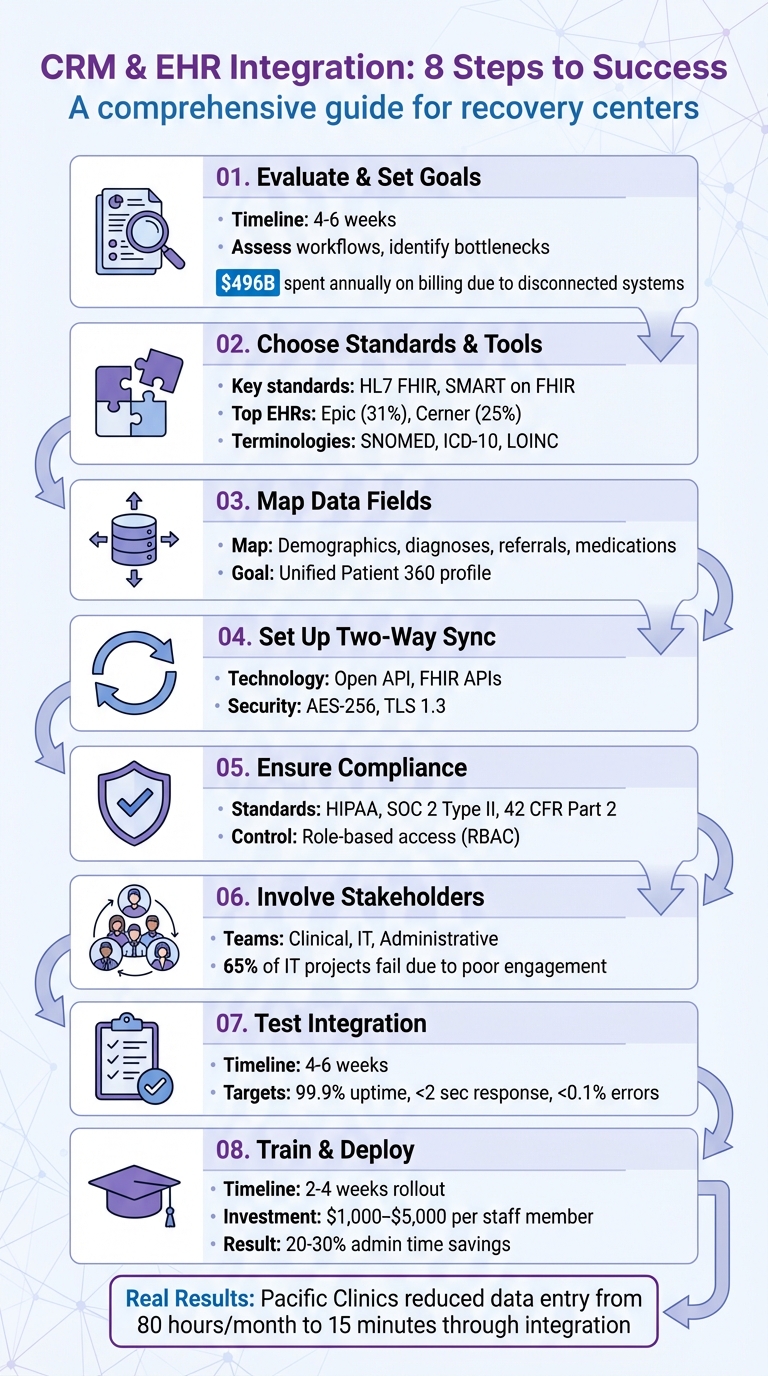
8-Step CRM and EHR Integration Process for Recovery Centers
Creating a Cohesive Patient Journey with a CRM-EHR Integration || LeadSquared Webinars
Evaluate Your Current Systems and Set Clear Goals
Before integrating your CRM and EHR, take a close look at your current systems to uncover inefficiencies. Many recovery centers still rely on outdated manual processes, which can lead to errors and wasted time. In fact, healthcare providers in the U.S. spend around $496 billion annually on billing and insurance costs, much of it stemming from disconnected systems. Dedicating four to six weeks to assess your workflows can highlight where data bottlenecks occur, where staff duplicate efforts, and where patients may slip through the cracks. This evaluation forms the foundation for identifying specific workflow challenges.
Find Problems in Your Current Workflows
Start by mapping out every step your team takes - from the first patient call to treatment and even alumni care. Look for areas where data gets stuck, such as clinical notes being confined to the EHR while communication logs are stored elsewhere. These silos can cause issues like the front desk unintentionally contacting the same person twice or a clinician missing key details that a patient has already shared with intake staff.
Legacy EHR systems often lack modern connectivity standards like HL7 FHIR, meaning middleware is often needed to bridge the gap. About 69% of independent providers report significant struggles in getting their EHR systems to integrate with other platforms. Additionally, compliance risks can arise when substance use disorder records are stored outside the EHR due to strict interpretations of 42 CFR Part 2. To address these challenges effectively, involve your clinical, administrative, and IT teams in documenting these pain points. This is especially critical, as 65% of healthcare IT projects fail due to poor stakeholder engagement.
Set Specific Integration Objectives
After identifying the issues, it’s time to define measurable goals for your integration efforts. Focus on objectives like reducing no-show rates, speeding up lead response times, and consolidating patient profiles so clients don’t have to repeat their story multiple times. Establish clear key performance indicators (KPIs) such as target response times, reductions in manual data entry, and improved patient retention rates. This will ensure that your investment - ranging from $30,000 to over $200,000 for complex systems across multiple facilities - delivers meaningful results.
Choose Compatible Standards and Tools
Once you've identified the gaps in your workflow and set clear goals, the next step is selecting the right technical standards and tools to ensure smooth communication between your CRM and EHR systems. Without shared "languages", data exchange can become a nightmare - or worse, you might end up with new silos that trap patient information in incompatible formats. Establishing this technical backbone is crucial for enabling standardized, real-time data sharing.
Use Standards Like HL7 or FHIR
HL7 FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) is widely recognized as the go-to standard for healthcare data exchange. It supports XML and JSON formats, making real-time API access much easier. Unlike earlier HL7 versions that relied on complex middleware, FHIR was built with web-based integration in mind. This allows you to pull essential data - like clinical notes, treatment plans, and discharge summaries - directly from your EHR.
SMART on FHIR takes things a step further by enabling third-party applications to operate directly within your EHR interface through standardized authentication. This means staff can seamlessly access CRM features - such as referral tracking or follow-up scheduling - without leaving the EHR environment. Leading EHR providers have embraced this approach: Epic, which holds a 31% market share, uses its App Orchard marketplace with SMART on FHIR, while Cerner, with a 25% market share, supports both SMART on FHIR and its own proprietary APIs.
To ensure your integration remains consistent and reliable, it's essential to adopt standardized terminologies. For clinical terms, use SNOMED; for diagnoses, ICD-10; and for lab results, LOINC. If your recovery center handles referrals to community-based organizations, the SDOH Clinical Care Implementation Guide can help. It uses FHIR APIs to exchange Social Determinants of Health data, addressing needs like housing, transportation, and employment.
Consider Recovery Center CRM for Integration
Building on these standards, Recovery Center CRM offers a tailored solution to meet the unique needs of recovery centers. This platform integrates effortlessly with EHR systems while adhering to strict HIPAA and SOC 2 Type II compliance standards. Its modern API connectivity reduces manual data entry and minimizes workflow disruptions. For example, intake coordinators can access treatment histories directly from the EHR, while clinicians can view referral statuses and communication logs without juggling multiple systems.
Recovery Center CRM supports widely used data formats like JSON, XML, and CSV, ensuring compatibility with major EHR providers such as Epic, Cerner, Allscripts, and athenahealth. Security is a top priority, with features like OAuth 2.0, OpenID Connect, AES-256 encryption, and TLS 1.3 ensuring safe data handling. For recovery centers that manage state-level reporting or justice system referrals, the platform centralizes documentation and tracks long-term outcomes across agencies. Role-based access control safeguards sensitive patient information, keeping it accessible only to authorized personnel.
Map Data Fields and Track Recovery Journeys
Once you've chosen the right technical standards and tools, the next step is mapping data fields to enable smooth CRM-EHR integration. This ensures patient information moves effortlessly between systems without creating errors or duplications. Proper mapping is key to avoiding fragmented records.
Align Key Data Elements Between Systems
After selecting your tools, the focus shifts to aligning data fields to maintain consistency. Start by identifying which fields need synchronization. For a full Patient 360 profile, include patient demographics like name, birth date, contact information, and housing status. Clinical data - such as diagnoses (ICD-10 codes), lab results, medication records (e.g., MOUD doses), and intake notes - should also be mapped. Don't overlook administrative fields, including insurance verification, referral sources (like hospitals, therapists, or courts), and consent records, which are essential for compliance with HIPAA and 42 CFR Part 2.
Additionally, standardizing the definition of a treatment episode is critical. Define a clear starting point, such as the biopsychosocial intake, and an endpoint, like the outpatient discharge date, that applies universally across all programs.
Track Long-Term Recovery Outcomes
Once your data fields are aligned, shift your focus to tracking recovery progress over time. Automating the tracking of recovery milestones can provide valuable insights. Map engagement metrics like appointment attendance, mood tracking, participation in 12-step meetings, and identified triggers. Set your CRM to automatically schedule check-ins at key intervals - 30 days, 90 days, and one year post-discharge - to maintain ongoing contact with alumni. This transforms data into meaningful insights that support recovery.
Platforms like Recovery Center CRM simplify this process by centralizing tracking. They automatically record treatment episode start and end dates, discharge instructions, and retention metrics across multiple programs. This unified system provides a clear view of recovery journeys, aiding both clinical and operational decisions. For centers handling state-level reporting or justice system referrals, this approach ensures consistent and accessible outcome data - eliminating the need for error-prone manual spreadsheets.
Set Up Two-Way Data Sync with Recovery Center CRM
Creating a two-way data sync between your CRM and EHR ensures a live, seamless connection where information flows in both directions. Clinical updates from the EHR will automatically appear in your CRM, while administrative changes made in the CRM are reflected back in the EHR.
Maintain Consistent Data Flow Across Systems
Two-way synchronization eliminates duplicate entries and keeps your data consistent. For example, when a clinician updates a diagnosis or adjusts medication dosages in the EHR, that information is instantly mirrored in your CRM. Similarly, if your admissions team modifies a patient’s contact details, verifies insurance, or updates satisfaction scores in the CRM, these changes are written back to the EHR.
This synchronization is powered by Open API technology, which connects the two platforms. As Kelly Arduino, Partner at Wipfli Advisory LLC, describes:
"Open API serves as a two-way bridge between separate software platforms, enabling you to import files across systems and create custom dashboards that combine all the patient health, billing and financial data needed to run your business more effectively."
This integration ensures your systems work together, avoiding fragmented records caused by isolated software.
For real-time updates, consider using FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) APIs. These APIs rely on modern web technologies to make health data modular and easily accessible. Before launching, test the sync in a sandbox environment using synthetic data and unique identifiers like MRN or MPI to avoid duplicate records.
Once the connection is stable, Recovery Center CRM takes integration a step further with its specialized features.
Use Recovery Center CRM's Integration Features
Recovery Center CRM simplifies the complexity of two-way data syncing by combining clinical and administrative workflows into a single, compliant platform. Designed specifically for recovery centers, the system automatically synchronizes clinical events - such as discharge instructions, MOUD (Medication for Opioid Use Disorder) changes, or new treatment episode start dates - from your EHR. At the same time, administrative updates, like scheduling a 90-day alumni check-in, are pushed back into the EHR without manual input.
The platform also automates key processes, like sending appointment reminders and follow-ups based on EHR data, helping to reduce no-show rates. To ensure data security and compliance, all transfers use AES-256 encryption for stored data and TLS 1.3 for data in transit. The system adheres to strict HIPAA and SOC 2 standards. Additionally, role-based access controls ensure that staff only see the data relevant to their specific responsibilities, whether they’re in admissions, clinical care, or alumni services.
Maintain HIPAA and SOC 2 Compliance During Integration
When integrating your CRM and EHR systems, securing every data exchange is non-negotiable. These systems constantly share patient information, which introduces risks that must be managed with strict safeguards. Both HIPAA regulations and SOC 2 certification require you to protect Protected Health Information (PHI) at every stage of the process.
To meet these standards, implement consent tracking and enhanced security measures aligned with HIPAA and 42 CFR Part 2 requirements. SOC 2 Type II certification adds an extra layer of assurance, as it validates that your security, availability, and confidentiality controls operate effectively over time. Controlling who accesses this sensitive data is the next critical step.
Set Up Role-Based Access Control
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) ensures employees only access the information they need for their specific roles. For example, front desk staff might only access schedules and contact details, billing teams would handle insurance information, and clinicians would see full treatment histories. Meanwhile, marketing teams should only view appointment statuses and consent indicators - without access to sensitive details like diagnoses or lab results.
Implement field- and record-level permissions to enforce a "least-privilege" approach. For instance, billing staff should not be able to view details such as HIV status or substance use diagnoses. Introduce "break-glass" controls that allow clinicians to access restricted records during emergencies, requiring them to provide a reason code that gets logged automatically. Use context-aware access restrictions to tighten control further, limiting access based on factors like IP address, physical location, device type, or time of access. Dual-approval workflows for PHI exports can also help mitigate the risk of insider threats and compromised accounts.
Once access is controlled, focus on securing data during transfer and storage.
Protect Data Transmission and Storage
Encrypt data at rest using AES-256 and secure data in transit with TLS 1.3. Use secure API connections that comply with HL7 FHIR standards, leveraging scoped credentials and syncing only the necessary fields. For mobile access, implement TLS-only endpoints, HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS), and certificate pinning to prevent interception attacks.
Maintain immutable, timestamped audit logs that capture every action involving PHI - whether it’s viewed, edited, exported, or deleted. These logs are invaluable for forensic investigations. Set up real-time alerts for unusual activity, such as bulk data exports at odd hours or from unauthorized roles.
Recovery Center CRM simplifies this process by automating these security measures, ensuring full HIPAA and SOC 2 compliance. This lets you focus on delivering patient care while maintaining robust data protection throughout the integration process.
sbb-itb-ce23a48
Involve Stakeholders to Align Workflows
Integrating new systems in a recovery center isn’t just about the technology - it’s about the people who use it daily. To make the integration work, you need input from administrators, program coordinators, and healthcare providers right from the start. Their involvement ensures the system aligns with your center's unique needs and reduces resistance during implementation.
"Most of the time, it's not the technology that causes a project to fail. It's the lack of preparation for tough organizational and technical issues." – Kandasoft
Start by gathering clinical leadership, IT teams, and frontline staff during the initial planning phase. These diverse perspectives can uncover workflow issues you might otherwise miss. For example, your admissions team might still rely on spreadsheets, while clinicians enter data directly into the EHR. This disconnect can lead to errors and wasted time - problems you can address early with the right input.
Review Workflows with Your Teams
Take a close look at your current workflows, including intake, referrals, scheduling, and follow-up processes. Document these steps to identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement.
Talk to your staff to uncover daily challenges. Ask targeted questions: How many clicks does it take to complete a referral? Where do repetitive tasks slow things down? What information is hard to find when it’s needed most? These conversations will guide you in designing a system that reduces administrative headaches.
Another helpful strategy is to create a network of "super-users" within your clinical teams. These individuals receive advanced training and can provide peer-to-peer support during the transition. Coastal Treatment Services successfully used this approach to overcome staff resistance, leading to better system adoption. By combining these insights with technical planning, you can create a smooth integration process.
Connect IT and Operations Teams
Your IT team knows the technical side - APIs, FHIR standards, and data security - while your operations team understands the day-to-day realities of patient care and scheduling. To build a system that works in practice, you need both perspectives.
Appoint a project leader who can bridge the gap between clinical needs and technical requirements. Without this role, you risk creating a system that’s technically sound but impractical for daily use.
Collaboration between IT and operations is key.
"Integration of siloed data... is essential to an efficient hub-and-spoke model of care, which must standardize and coordinate patient care across multiple clinics and departments." – Addiction Science & Clinical Practice
Set up regular feedback loops between IT consultants, clinical leaders, and operational staff. Weekly meetings during development can catch usability issues early, giving you time to make adjustments before a full rollout. Focus on practical concerns: Does the interface minimize clicks? Can staff access the information they need quickly? Are automated triggers working as expected?
Recovery Center CRM simplifies this process by offering a platform tailored to recovery centers. Its customizable features let you adapt workflows to fit your needs while staying compliant with HIPAA and SOC 2 standards. This way, your IT and operations teams can focus on aligning processes without the added burden of building integrations from scratch. With this collaborative groundwork in place, you’ll be better prepared for system testing and staff training in the next phases.
Test Integration Across All Key Features
Once workflows are aligned and teams are connected, set aside 4–6 weeks to thoroughly test and validate the integration. This period gives you enough time to identify bugs, confirm data accuracy, and collect user feedback.
Use isolated testing environments to protect live patient data during these trials. These "sandbox" setups allow your team to simulate real-world scenarios without compromising your operational systems. From there, focus on testing the core functions that are critical to seamless integration.
Test Core Functions
Start by ensuring bi-directional data synchronization between your CRM and EHR. Clinical data, such as diagnoses and lab results, should flow smoothly from the EHR to the CRM. At the same time, administrative updates, like changes to contact information, need to sync back to the EHR. Test every step of your lead management pipeline, from the initial inquiry to screening, insurance verification, and final admission, to ensure no prospective patient is overlooked.
Confirm that Patient 360 profiles provide a complete picture by consolidating demographic details, clinical histories, medications, and logs into a single, unified view. Automated engagement tools, such as appointment reminders and care plan follow-ups, should also trigger correctly based on EHR data. During testing, aim for top-tier performance metrics: 99.9% system uptime, response times under two seconds, and error rates below 0.1%. Use automated monitoring tools to track these benchmarks in real time.
Fix Errors and Bugs
Conduct user acceptance testing (UAT) with clinicians and administrators to uncover usability issues that may not surface during technical testing. Their hands-on experience can reveal workflow disruptions that might otherwise go unnoticed. Keep detailed change logs to document and address bugs as they arise.
Verify data accuracy at every integration point, watching for issues like duplicate profiles, missing fields, or formatting inconsistencies. Use comprehensive audit logs to identify where data transfers break down. For particularly complex data mapping challenges, middleware can simplify the process. Recovery Center CRM, for example, offers built-in integration tools tailored for recovery centers, easing the technical workload while adhering to strict HIPAA and SOC 2 standards.
Roll Out the System with Staff Training
Deploy your integrated system within a 2–4 week window. Plan to invest $1,000–$5,000 per staff member for hands-on, role-specific training.
Mountain View Recovery saw impressive results after their rollout: a 40% reduction in documentation time, 28% faster insurance verification, and annual savings of $120,000 within six months. These outcomes highlight the importance of prioritizing training. Be prepared for a temporary dip in productivity as staff adjust. This initial phase is critical for setting up effective, role-based training.
Create Training Programs for Staff
Begin by identifying "super-users" - key staff members like therapists, nurses, and administrative personnel - who will undergo advanced training. These individuals can then support their peers with guidance and troubleshooting.
Spread training sessions over several weeks. Use a sandbox environment to tailor the experience: clinicians can focus on clinical workflows, while billing staff work on mastering revenue cycle tasks. Highlight the benefits of the system, such as eliminating duplicate data entry, automating reminders, and providing quick access to accurate information. Well-structured training improves efficiency and enhances patient tracking.
"The more comfortable your team is with the software before go-live, the smoother the transition will be." - BehaveHealth
For the first 24–48 hours post-launch, reduce clinician schedules to ease the transition. Implement daily huddles or an online ticket system to address issues in real time and make immediate adjustments based on staff feedback.
Deploy in Stages
Once staff are comfortable, roll out the system in phases to fine-tune operations across departments. Start with a pilot group to gather real-time feedback and resolve any issues before expanding to other areas. This gradual approach minimizes risks and ensures smoother implementation.
Schedule formal evaluations at 3 and 6 months after the rollout to assess whether the system is achieving key goals, such as reducing documentation time or billing errors. Use feedback from each stage to refine the system further. Maintain a supportive tone from leadership, encouraging a collaborative mindset and open communication to ease concerns and foster confidence.
Monitor Performance and Make Improvements
Once your CRM and EHR integration is live, keeping a close eye on its performance becomes essential. Automated dashboards can help you track real-time technical and business metrics, giving you a comprehensive Patient 360 view.
Pay attention to four key areas: technical performance, user adoption, data quality, and business impact. Many organizations report 20-30% savings in administrative time after a successful integration.
Measure Key Performance Indicators
To gauge the success of your integration, start with clear, measurable benchmarks. Establish pre-integration baselines, such as workflow speeds and error rates, to compare improvements post-launch. For instance, Pacific Clinics in California collaborated with Provisio in 2024 to integrate their EHR and CRM systems. This effort cut a manual data entry process from 80 hours a month to just 15 minutes through automation.
Track both technical and clinical outcomes. Metrics like medication error rates, treatment plan adherence, and long-term recovery retention help evaluate the impact on patient care. Integrated EHR systems, for example, have been shown to reduce medication errors by an average of 48.8%. Patient engagement is another critical area - monitor no-show rates and patient portal logins. Automated reminders, used by nearly 90% of healthcare practices, are linked to reduced no-show rates.
For technical performance, aim for 99.9% system uptime, response times under 2 seconds, and error rates below 0.1%. Data quality metrics, such as accuracy and completeness, should also remain a priority. These benchmarks not only measure success but also provide a foundation for gathering feedback and making necessary adjustments.
Use Feedback for Ongoing Improvements
Numbers tell part of the story, but qualitative feedback from staff can uncover hidden challenges. Surveys are particularly effective for identifying workflow bottlenecks that metrics alone might miss. For example, Denver Health integrated substance use disorder (SUD) treatment data into their Epic EHR between July 2021 and May 2022. Three months after the full launch, a survey of 38 addiction therapists (with a 68% response rate) revealed key insights. Therapists at Federally Qualified Health Centers found the new documentation process more burdensome, while Emergency Department staff highlighted the need for better visualization of patient care linkages outside their system. These findings helped leadership address specific departmental issues and training needs.
To streamline ongoing improvements, create a network of "super-users" - staff members who can offer peer support and share informal feedback on daily workflows. Schedule formal evaluations at 3 and 6 months post-launch, and maintain consistent oversight with recurring reports on clinical outcomes and revenue metrics. Regular data validation reports ensure that synced information between the CRM and EHR remains accurate and consistent. Additionally, periodic access control reviews help safeguard data security as staff roles evolve over time.
Conclusion
Integrating CRM and EHR systems can reshape how recovery centers operate and care for their patients. By combining clinical history with engagement data into a unified Patient 360 profile, your team gains a comprehensive view of each individual's recovery journey - from their first inquiry to long-term success. These unified records become the foundation for delivering better care and achieving measurable results.
Real-world examples highlight the benefits of integration. Both Pacific Clinics and Denver Health have shown how this approach reduces manual tasks while improving patient retention rates.
To implement integration successfully, careful planning is key. Start by reviewing your workflows and setting clear objectives. Opt for systems that adhere to standards like HL7 FHIR to ensure smooth data exchange. Map out data fields carefully, enforce compliance with HIPAA and SOC 2 through role-based access controls, and involve your team at every stage. Testing, staff training, and ongoing monitoring are crucial for long-term success.
"Integration of siloed data... is essential to an efficient hub-and-spoke model of care, which must standardize and coordinate patient care across multiple clinics and departments."
As value-based care becomes more prevalent and patients expect more personalized communication, integration is no longer optional. By addressing these challenges thoughtfully, recovery centers can streamline operations, reduce errors, and focus on what truly matters - helping individuals on their journey to recovery.
FAQs
What are the benefits of integrating CRM and EHR systems in recovery centers?
Integrating CRM and EHR systems in recovery centers brings a host of benefits by merging clinical and operational data into a single platform. This unified approach allows providers to access a comprehensive "Patient 360" profile, which includes everything from medical history and communication records to scheduling and care plans - all in one place. With this centralized view, staff can offer more tailored care, engage patients more effectively, and ultimately improve treatment outcomes.
Efficiency also gets a significant boost. Tasks like outreach, case management, and data entry can be automated, saving time and reducing the risk of errors. Plus, it helps ensure compliance with privacy regulations like HIPAA. Integrated systems make it easier to monitor long-term outcomes and create impact reports, which are vital for showcasing success and securing funding. In short, this integration not only simplifies operations but also maximizes resources, enabling recovery centers to provide better support for individuals on their path to recovery.
What steps can recovery centers take to ensure HIPAA and 42 CFR Part 2 compliance when integrating CRM and EHR systems?
To comply with HIPAA and 42 CFR Part 2 during CRM and EHR integration, recovery centers need to prioritize stringent data privacy and security practices. This means obtaining patient consent before sharing substance use disorder (SUD) records, except in legally allowed situations, and ensuring sensitive information is protected through secure methods like encryption and strict access controls.
Recovery centers should also remain informed about regulatory updates and ensure their systems are equipped to handle lawful SUD data sharing. Key steps include creating clear policies for re-disclosure, maintaining thorough documentation of data-sharing activities, and training staff on compliance protocols. Tools such as Recovery Center CRM, built with HIPAA and SOC 2 compliance in mind, can simplify these efforts. These platforms offer secure workflows and consent management features, helping recovery centers coordinate care effectively while maintaining patient confidentiality.
What key technical standards ensure smooth data exchange between CRM and EHR systems?
To facilitate seamless data exchange between CRM and EHR systems, adopting HL7 FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) is a must. This standard is widely used for secure and efficient health data sharing. FHIR supports real-time data synchronization through modern web technologies like JSON and XML, making it particularly suited for recovery centers aiming to improve long-term patient care.
Incorporating standardized medical terminologies such as SNOMED, ICD-10, and LOINC is equally important. These ensure clinical data is interpreted consistently across different systems. On top of that, implementing robust APIs, maintaining version control, and strictly adhering to HIPAA compliance - with practices like end-to-end encryption and detailed audit trails - adds an essential layer of security and reliability.
By embracing these strategies, recovery centers can simplify workflows, safeguard sensitive data, and improve the quality of care they provide.

